How do I...?
Community History |
Frequently Asked Questions |
Local History Materials |
Image Gallery
Community Links |
Library History |
Community Profile
 Lakewood is a city ten miles
southeast of Los Angeles that in 1950 broke new ground-literally and
figuratively-when the Lakewood Park Company started building what would become
the nation's first post-war planned housing development, consisting of 17,500
houses on about 3,500 acres. Lakewood emerged from a former sugar beet field
to become a model planned community, complete with street lighting and
underground wires, assembly-line construction of about 50 houses a day, berms
between residential streets and the highway, and a car-friendly prototype
shopping area called Lakewood Center.
Lakewood is a city ten miles
southeast of Los Angeles that in 1950 broke new ground-literally and
figuratively-when the Lakewood Park Company started building what would become
the nation's first post-war planned housing development, consisting of 17,500
houses on about 3,500 acres. Lakewood emerged from a former sugar beet field
to become a model planned community, complete with street lighting and
underground wires, assembly-line construction of about 50 houses a day, berms
between residential streets and the highway, and a car-friendly prototype
shopping area called Lakewood Center.
The community's size also eclipsed that of many long-established cities such as Holyoke, Massachusetts, and Santa Ana, California. Promoted with slogans such as "Lakewood - My Home Town" and "Lakewood, Tomorrow's City Today," the community was built just in time for war veterans and their families to buy their first homes with the help of the G.I. Bill of Rights, which let buyers put little or no money down and pay for their mortgages with low-interest 30-year loans.
 As the unincorporated Lakewood grew from a small village in 1950 to a community
of more than 70,000 residents in less than three years, so grew its municipal
needs. Lakewood thus had three choices: become annexed to nearby Long Beach,
remain unincorporated and continue to receive county services, or incorporate
as a city. In 1954, residents chose the latter option and voted to incorporate
as a city, the largest community in the country ever to do so and the first
city in Los Angeles County to incorporate since 1939.
As the unincorporated Lakewood grew from a small village in 1950 to a community
of more than 70,000 residents in less than three years, so grew its municipal
needs. Lakewood thus had three choices: become annexed to nearby Long Beach,
remain unincorporated and continue to receive county services, or incorporate
as a city. In 1954, residents chose the latter option and voted to incorporate
as a city, the largest community in the country ever to do so and the first
city in Los Angeles County to incorporate since 1939.

However, the incorporation had a twist: while the new City Council would set policy and budgets at the local level, members would continue to contract with Los Angeles County to receive a wide range of county services such as road repair, water and sewer services, and fire protection. This novel arrangement-which let the city retain local control of its government while tapping efficiently into existing services-was spelled out in a document called the Lakewood Plan, that was adopted and modified by many other communities in California and the United States that wanted to incorporate as well.
 Today Lakewood-with 26,000 housing units, most of them single-family detached
homes-remains known for its community services and quality of life as a bedroom
community. The community is studied by historians and city planners because
of its distinction as a ground-breaking type of suburb and because of the
Lakewood Plan's visionary combination of local and county services. Among
other things, Lakewood introduced a number of innovations into suburban
development-such as assembly-line house construction-and is often compared to
Levittown, New York. More information about Lakewood can be found in the
following sources:
Today Lakewood-with 26,000 housing units, most of them single-family detached
homes-remains known for its community services and quality of life as a bedroom
community. The community is studied by historians and city planners because
of its distinction as a ground-breaking type of suburb and because of the
Lakewood Plan's visionary combination of local and county services. Among
other things, Lakewood introduced a number of innovations into suburban
development-such as assembly-line house construction-and is often compared to
Levittown, New York. More information about Lakewood can be found in the
following sources:
Website Links:

Print Sources:
- Klissner, Harry. How Agencies of Communications Can Convert a Gigantic Real Estate Operation (Lakewood) into a Socially Cohesive Community. M.A. thesis. Los Angeles: University of California, Los Angeles, 1954.
- Wentz, John Budd. An Analysis of the Advisability of Annexing All or a Part of the Lakewood Area to the City of Long Beach. M.A. thesis. Los Angeles: University of Southern California, 1951.
- Todd, John S. A History of Lakewood, 1949-1954. Lakewood, CA: Lakewood City Hall, Public Information Office, 1984.
- Waldie, D. J. Holy Land: A Suburban Memoir. New York: W.W. Norton, 1996.
Images:
- Aerial view of tract homes and Lakewood Center, 1964
[Courtesy of the City of Lakewood] - Aerial view looking north on Lakewood Boulevard at Carson Street, 1935
[Courtesy of the City of Lakewood] - Aerial view of Lakewood with houses under construction, 1989
[Courtesy of Lakewood Living] - Aerial view of Lakewood, 1959
[Courtesy of the City of Lakewood] - Yellow decal in a daisy shape that asks Lakewood residents to 'Keep Lakewood Fresh as a Daisy', c. 1968
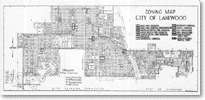
[Courtesy of the City of Lakewood] - Zoning map showing City of Lakewood zoning districts, 1971
[Courtesy of the City of Lakewood]
![]()
Agoura Hills |
Antelope Valley |
Carson |
Catalina Island |
Claremont |
East Los Angeles
Gardena |
Lakewood |
La Puente Valley |
Pico Rivera |
San Dimas |
San Fernando
San Gabriel |
South Gate |
Willowbrook





